BACKGROUND:
Who can say that they have never burned biscuits in the oven? Apart from the terrible smell and growing appetite, the potential for starting a fire or receiving a thermal burn are serious concerns. When it comes to burns, there are three major types, which includes thermal burns, electrical burns, and chemical burns. Thermal burns are caused by contacting an object that has enough heat on the surface to cause injury. Electrical burns are received through direct or non-direct contact with a pathway of electricity. Chemical burns are typically observed during the use of corrosive materials or acids, such as industrial solvents or cleaning products. During February 5th – February 11th burn awareness is a national topic. The goal of this article is to provide a better understanding of the hazard that is burns as well as providing protection factors that will prevent you and your fellow worker from being exposed to a burn.
UNDERSTANDING THE HAZARDS:
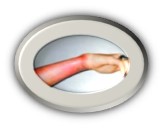
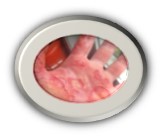
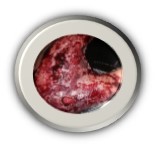
Each year in the United States, 1.1 million burn injuries require medical attention. From this 1.1 million, it is estimated that up to 10,000 people will die from burn-related infections. This supports the fact that the initial burn itself may not be fatal, but improper after care can result in devastating losses. Typically, when burns are discussed, it is thermal or contact burns as the primary culprit. However, contact with chemicals or electricity can result in severe burns as well. Most burns are relatively small and are classified as minor. These burns tend to share common symptoms, such as pain at the location of the burn. When more extensive and deep levels are reached, then they are classified as severe burns, which can result in the need to seek immediate care, specifically trauma units. Where do most burns occur? Well, the skin is the largest organ of the body and typically this is where burns are commonly reported. The skin has major functions, which includes protection from elements and liquid retention. When the skin has become damaged and can no longer function properly, further issues can arise such as infection, headaches, and trouble breathing. Based on the degree of the burn, which ranges from 1st, 2nd, or 3rd different first aid or medical attention is required. 1st degree burns are common like a sunburn or rug burn. 2nd degree burns are the most painful, as the nerve ending is affected but not destroyed completely. 3rd degree burns are the most devastating as all layers of the skin have been damaged beyond repair. 3rd degree burns are highly subject to infections.
UNDERSTANDING THE PROTECTION FACTORS:
Before any operations are conducted, ensure proper pre-planning has taken place. Based on the hazards identified and operations to be conducted training should be up to date, which should include a component on hazard identification, as things may change during the timeline of operations. Anytime there is a potential for fire a properly rated and fully charged fire extinguisher should be present in the working zone. Training on proper usage should be up to date as well for the affected employees. When operations involve working with or near electricity, ensure proper protection factors are present, such as outlet covers. Live panels should have face plates and all knock-plates present. Any openings should be protected to prevent arc of electricity. When utilizing chemicals, always follow the manufacturer’s recommendations of firefighting measures and proper handling of said chemical. The SDS of a chemical will provide information on specific personal protective equipment that should be provided for safe operations. Always try to eliminate the hazard or change how the operations are conducted to limit exposure levels, if possible, as personal protective equipment is the last line of defense.
Heightened awareness is always a key to successful activities. A multitude of operations will require workers to be exposed to potential hazards that may cause burns. Ensure your first aid kit is stocked with items associated with the work atmosphere. Burn cream and gauze are necessary items in this regard. Discuss with your workers the hazards involved in any activities, but especially when hot surfaces, boiling liquids, corrosive chemicals, or live current is part of the equation. Communicate the importance of these protection factors and require employees to wear proper personal protective equipment at all times.
Related Topics: Safety Tips, Accident Prevention, Safety Articles, Monthly Safety Topics, Fire Prevention