As the construction season ramps up, it is important for companies to be prepared by conducting equipment training before an incident resulting in a negative outcome occurs. For common types of construction equipment, the following is a breakdown of the rules and standards set forth by both OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) as well as ANSI (American National Standards Institute).
Aerial Lifts/Work Platforms have been renamed and are now called Mobile Elevating Work Platforms (MEWP). Aerial lifts used to be classified as scissor lifts, boom lifts, etc., but now, they will be classified into “Group A” or “Group B” as well as “Type 1, Type 2, or “Type 3”.
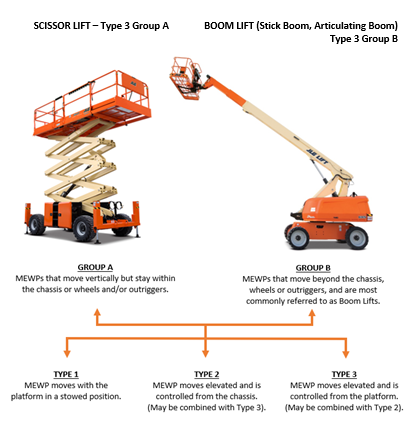 GROUP A: MEWPs that move vertically but stay within the chassis or wheels and/or outriggers.
GROUP A: MEWPs that move vertically but stay within the chassis or wheels and/or outriggers.
GROUP B: MEWPs that move beyond the chassis, wheels, or outriggers, and are most commonly referred to as Boom Lifts.
TYPE 1: MEWP moves with the platform in a stowed position.
TYPE 2: MEWP moves elevated and is controlled from the chassis. (May be combined with Type 3).
TYPE 3: MEWP moves elevated and is controlled from the platform. (May be combined with Type 2).
OSHA (Standard Requirements)
1926 Subpart L 1926.453 – Aerial Lifts
All operators and occupants of the equipment who fall within this standard need to be familiar with the specific equipment. The training consists of classroom instruction followed by a hands-on evaluation. Refresher training also plays a key role in avoiding potential on the job accidents and injuries. Refresher training is recommended when an accident occurs during aerial lift use, workplace hazards are discovered, or a different type of aerial lift is used.
ANSI (Best Practices)
As of June 1st, 2020, ANSI has updated the standard for MEWP (Mobile Elevated Work Platforms) regarding users, operators, occupants, and supervisors. Although ANSI standards have been updated, they are not yet adopted by OSHA and therefore, are to be followed as consideration to best practices in construction activities.
ANSI’s newest set of recommendations indicate that training should be a formalized equipment familiarization with specific equipment as opposed to the general type of equipment referencing the overall safety activities. OSHA still follows the equipment-type of training, and though they have not yet adopted these rules, preparing for that change in advance is always a good idea.
The primary reason changes were made stemmed from concern outlined in multiple appeals regarding modifications or additions to an MEWP could only be made with the permission of the manufacturer, and that the Manual of Responsibilities be placed on every Mobile Elevating Work Platform.
TRAINING – WHAT CHANGED?
According to ANSI A92.24 - 2018, the following should be adhered to as a Best Practice until the standard is officially adopted by OSHA:
Operators, supervisors, occupants and users/owners must be trained by a qualified person and in a language all trainees can understand.
OPERATORS: Operators must be physically and mentally capable to operate the equipment. They must be trained, familiarized, and authorized to operate specific equipment relative to their work. Operators must know:
- Where to find operator manuals for the type and class of equipment.
- Purpose of each control, feature, and device.
- The limitation of equipment and operating characteristics.
SUPERVISORS: Any personnel who directly supervises operators must be identified and trained. Supervisors must know:
- Proper MEWP selection for type of work performed.
- Rules, regulations and standards for all types of MEWPs, including safe use, training and familiarization and the work being performed.
- Identifying potential hazards and control methods to protect against them.
- Understanding of the importance of specific MEWP Operations Manuals and storage of manuals, easily accessible to operators.
OCCUPANTS: Occupants do not have authority to operate the equipment except in the case of an emergency. If the operator becomes incapacitated, the occupant must be able to operate the controls. Occupants require a basic overview and a basic level of knowledge to work safely on the equipment.
USER/OWNER: If a user/owner sells, leases, or rents any kind of MEWP for use, that user or owner must either offer the training to the operator or advise operators where training may be obtained. The user/owner must maintain a proof of training and familiarization for any employees who are authorized to operate an MEWP.
Essentially, each piece of equipment is different based on Group and Type classifications and must be evaluated individually with each operator.
TRAINING RECORDS:
The following must be retained by employers:
- The name of the person(s) trained: supervisor, operator, or occupant. Signatures by all parties must be included on the Sign-In Log.
- Supervisor: must be trained in their roles and responsibilities.
- Operator: must be trained to the specific type of equipment with a formal familiarization process.
-
- Occupant: must review controls to operate in case of emergency.
- Company or individual providing the training/equipment evaluations.
- Date of training.
- MEWP classification (Boom Lift, Scissor Lift, Aerial Lift, etc.).
- ANSI Classification (i.e.: Type 3, Group A).
RESCUE PLANNING:
A written Rescue Plan must be included in formal training instruction. To plan for potential emergencies, such as falls from the platform, equipment breakdown or a platform entanglement, pre-planning rescue methods is critical. The 3 primary types of rescue include:
- SELF-RESCUE: By individual involved.
- ASSISTED RESCUE: By others at the worksite.
- TECHNICAL RESCUE: By EMS, Fire Service, or other emergency personnel.
OTHER REQUIREMENTS:
Inspections must be conducted to identify and correct any hazards or malfunctions. These inspections (Frequent, Annual) must be performed by a qualified person and a Pre-Start inspection must be performed by the operator. Equipment should not be used until or unless inspections indicate equipment is operationally safe.
- FREQUENT INSPECTION: Conduct prior to placing equipment into service or if the equipment has been out of service longer than three months.
- ANNUAL INSPECTION: Perform at least every 12 months, and include items from frequent inspection list as well as the manufacturer’s specified list.
- PRE-START INSPECTIONS: Each day or at the start of each shift.
SUMMARY
As this construction season is upon us, taking the time to understand both requirements as well as best practices relative to MEWP and ensure all involved parties are trained and ready for operation is much simpler to manage proactively. Staying ahead of changes helps the sometimes overwhelming implementation as new standards are adopted, and keeping workers safe and healthy should always be our focus.
For more information regarding customized procedures, employee training or general questions about this information, please reach out to info@safetyresources.com.
Related Topics: Safety Staffing, Safety Consulting, Safety Tips, Jobsite Safety, Safety Training, Aerial Lifts, Monthly Safety Topics